The primary purpose of industrial protective coatings is to create a barrier between the substrate and the surrounding environment. They offer resistance against corrosion caused by moisture, chemicals, or harsh weather conditions. Additionally, these coatings can provide protection against physical wear and tear, impact damage, and exposure to UV radiation. Industrial protective coatings can also offer specific properties such as fire resistance, anti-slip surfaces, chemical resistance, or insulation.
By safeguarding the underlying substrate, these coatings help extend the service life of industrial assets, reduce maintenance requirements, and improve overall operational efficiency. Proper surface preparation and application techniques are crucial for the successful implementation of industrial protective coatings, ensuring optimal adhesion and performance.
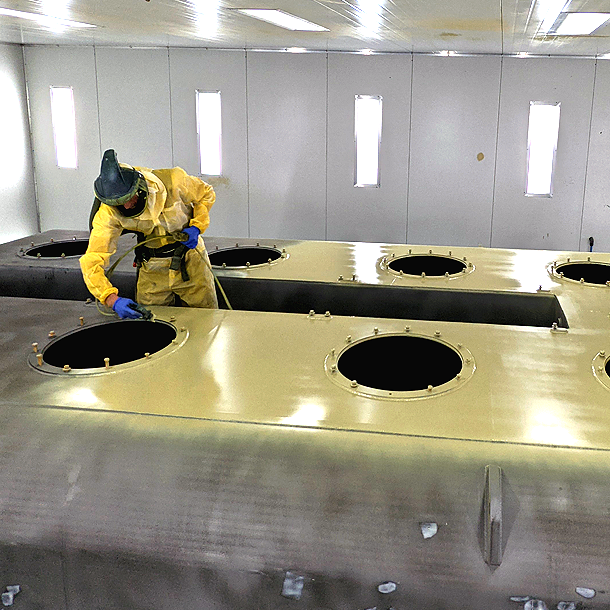


Surface Preparation: Proper surface preparation is essential for the successful application of industrial protective coatings. The surface to be coated is cleaned thoroughly to remove any dirt, grease, rust, or existing coatings. This may involve methods such as pressure washing, sandblasting, or chemical cleaning. Surface preparation ensures optimal adhesion of the protective coating and helps remove any contaminants that could compromise the coating’s performance.
Primer Application: A primer is often applied as the initial layer before the main protective coating. The primer helps improve adhesion, enhances corrosion resistance, and promotes uniform coverage of the final coating. The primer is applied using suitable application methods such as spraying, brushing, or roller coating. The choice of primer depends on the specific requirements of the substrate and the protective coating system being used.

Main Coating Application: The main industrial protective coating is applied once the primer has cured. The coating material is chosen based on the desired properties, such as corrosion resistance, chemical resistance, UV resistance, or impact resistance. The coating can be applied using various techniques, including spraying, brush or roller application, or specialized coating methods such as powder coating or hot-dip galvanizing. Proper application techniques, including maintaining the correct film thickness and ensuring uniform coverage, are crucial to achieving the desired protective properties.

Curing and Drying: After the main coating application, the coating is allowed to cure and dry. This involves providing the necessary time for the coating material to chemically bond and harden. The curing process can vary depending on the type of coating being used, and it may involve air drying, heat curing, or exposure to specific curing agents. Proper curing ensures the coating’s full protective properties are developed and maximizes its durability and longevity.

Inspection and Quality Assurance: Once the coating has cured, a thorough inspection is conducted to ensure proper adhesion, coverage, and quality of the industrial protective coating. This involves visually examining the coated surface for any defects, irregularities, or areas that may require touch-ups. Additionally, quality tests such as adhesion tests, thickness measurements, or specific performance tests may be performed to ensure the coating meets the required standards and specifications.
In many cases, the materials most suited to building machinery are also likely to corrode. Sometimes the materials that pass through these machines are the ones causing corrosion. The only way to avoid this problem is through the use of industrial coatings, which can be engineered to provide the perfect connection between machine and the material being processed.
© 2024 RAB ltd | Website Design by iFactory